 Pressure sensors are pivotal components in various industrial applications, playing a crucial role in monitoring and controlling pressure levels in diverse environments. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global pressure sensor market is projected to grow from USD 4.93 billion in 2021 to USD 6.68 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for automation in industries such as oil and gas, automotive, and healthcare, where precision in pressure measurement is essential for optimal performance and safety.
Pressure sensors are pivotal components in various industrial applications, playing a crucial role in monitoring and controlling pressure levels in diverse environments. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global pressure sensor market is projected to grow from USD 4.93 billion in 2021 to USD 6.68 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for automation in industries such as oil and gas, automotive, and healthcare, where precision in pressure measurement is essential for optimal performance and safety.
These sensors come in various types, including piezoresistive, capacitive, and optical pressure sensors, each with unique applications suited for different industry needs. For instance, piezoresistive sensors are widely used in medical devices and automotive applications due to their high sensitivity and accuracy. Meanwhile, capacitive sensors find their place in consumer electronics and industrial processes, offering robustness and reliability. The versatility of pressure sensors allows them to not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute significantly to process safety and reliability.
In summary, pressure sensors are integral to modern technology and industry practices, providing critical data that aids in decision-making and process optimization. As industries continue to evolve and seek greater efficiency, the relevance and demand for advanced pressure sensing solutions are set to increase significantly.
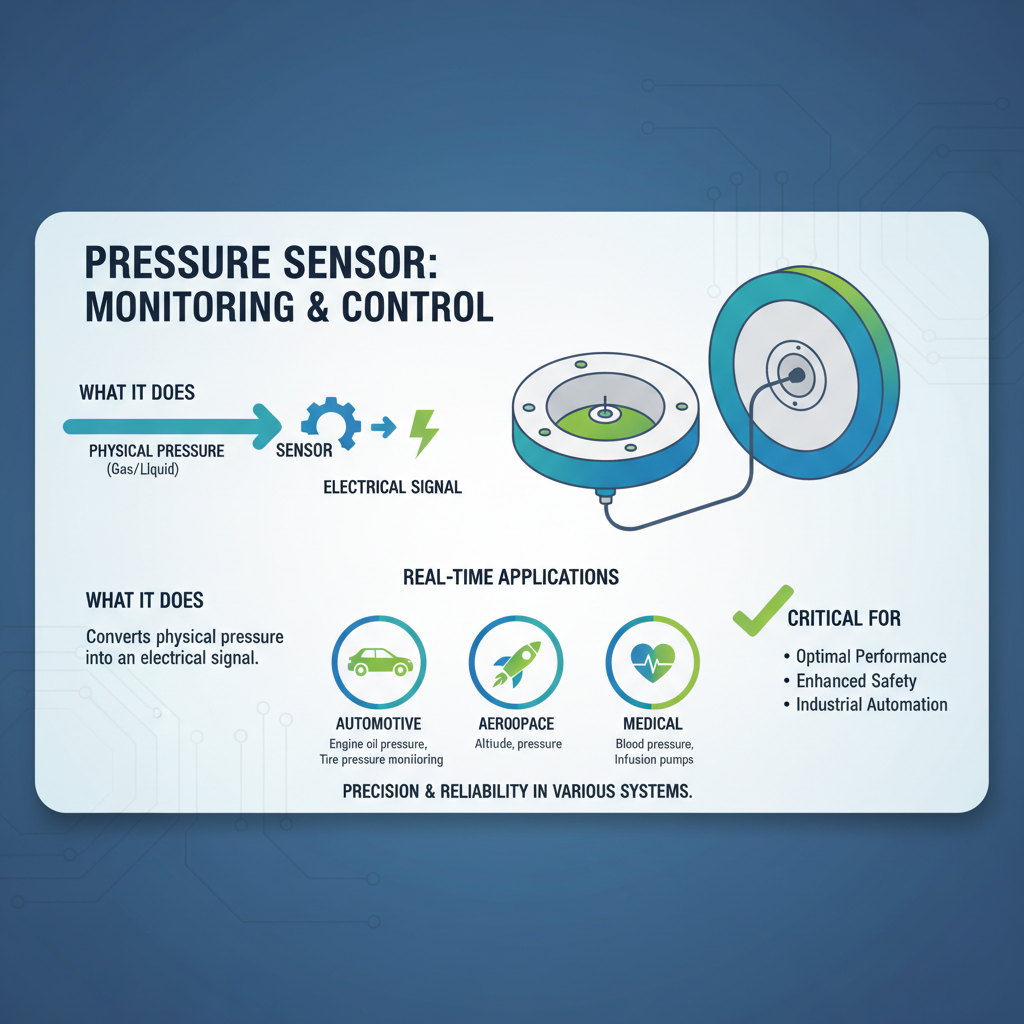
A pressure sensor is a crucial device used to measure the pressure of gases or liquids within various systems. Essentially, it converts a physical pressure into an electrical signal, allowing for real-time monitoring and control in different applications. These sensors play a vital role in numerous industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical sectors, where precise pressure measurements are critical for optimal performance and safety.
In the medical field, pressure sensors are increasingly redefining the landscape of healthcare technologies. They are integral to devices that monitor vital signs, assist in diagnostics, and manage complex therapies. Their functionality extends to applications such as ventilators, infusion pumps, and blood pressure monitors, where accurate pressure readings can significantly impact patient outcomes. With advancements in sensor technology, new trends are emerging, enhancing the capabilities of medical devices and expanding their applications, ultimately leading to better patient care and safety.
Pressure sensors have evolved significantly, leading to various types that cater to different applications. The primary types include piezoresistive sensors, capacitive sensors, and optical pressure sensors, each with unique working principles. Piezoresistive sensors, for instance, utilize the change in electrical resistance due to mechanical stress, making them ideal for applications that require precise pressure measurement in industrial settings. Capacitive sensors, on the other hand, detect changes in capacitance caused by pressure variations and are commonly used in consumer electronics and automotive industries. Optical pressure sensors leverage light transmission properties, offering high sensitivity and robustness, which suits them for challenging environments.
Tips: When selecting a pressure sensor, consider the operating conditions, such as temperature range, environment, and required accuracy. This ensures that the sensor chosen will perform optimally and meet specific application needs. Additionally, understanding the working principles of different sensor types can help in identifying the most suitable option for your project.
Recent advancements in technology, particularly in the realm of the Internet of Things (IoT), have propelled the development of flexible pressure sensors. These sensors are becoming widely applicable in smart devices, wearable technologies, and healthcare monitoring systems. Hence, staying updated on the latest sensor technologies is vital for professionals aiming to integrate these innovations into their designs.
Pressure sensors are crucial components utilized across various industries, acknowledged for their versatility and significance in modern technology. In the automotive sector, these sensors play a vital role in monitoring tire pressure, ensuring safety and efficiency. The aerospace industry also relies heavily on pressure sensors for altitude measurement and environmental monitoring, which are essential for flight safety.
In the healthcare field, pressure sensors are extensively used in medical devices such as ventilators and infusion pumps, where precise pressure readings are imperative for effective treatment. Additionally, the oil and gas industry employs pressure sensors to monitor well conditions, safeguarding against potential hazards. With the increasing demand for advanced monitoring systems across different applications, the growth of the pressure sensor market continues to accelerate, enabling improvements in safety, efficiency, and performance in numerous sectors.
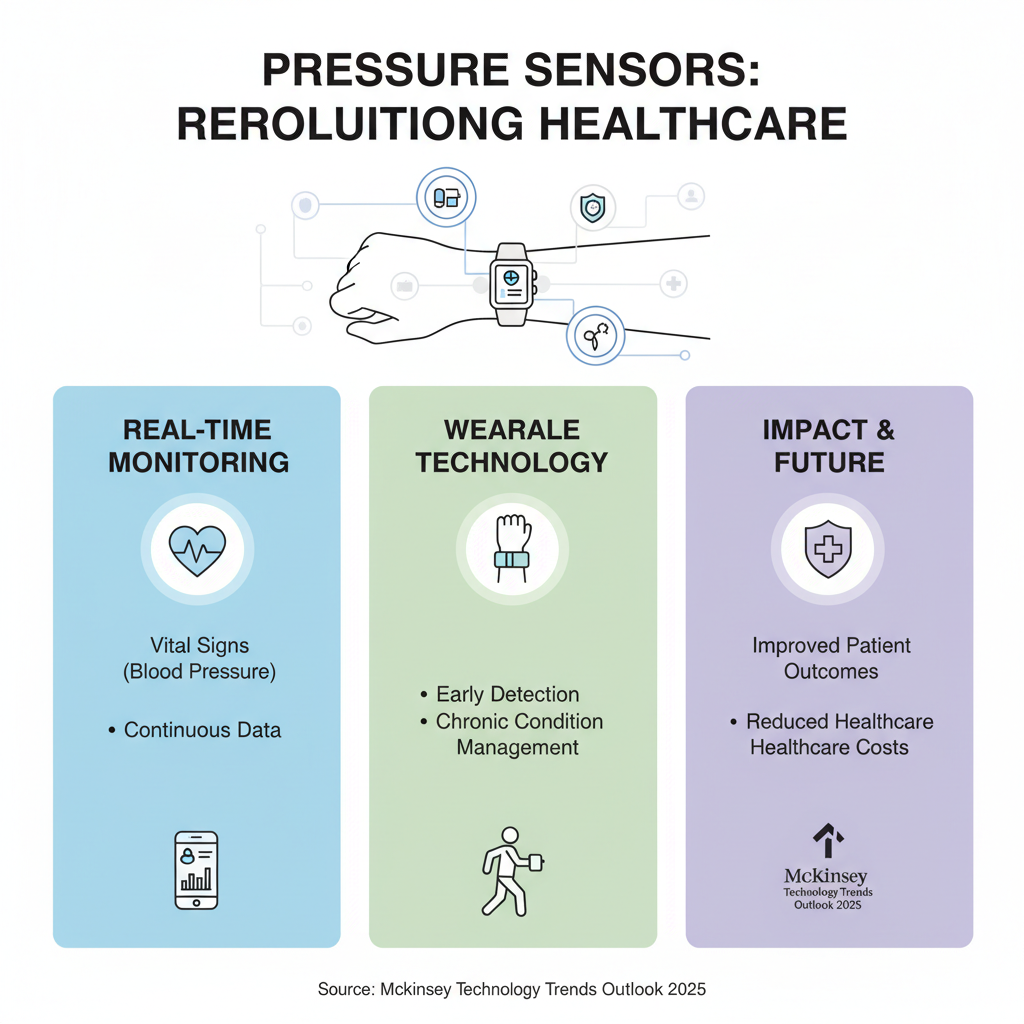
Pressure sensors play a crucial role in modern technology, particularly in the healthcare sector, where their ability to provide real-time data can significantly enhance patient care. With the increasing adoption of wearable technology, these sensors enable continuous monitoring of vital signs, including blood pressure, which is vital for early detection of health issues. A recent analysis from the McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2025 highlights that integrating pressure sensors in wearables can lead to better management of chronic conditions, ultimately reducing healthcare costs and improving outcomes for patients.
Moreover, advancements in pressure sensor technology have led to the development of devices that are not only more accurate but also capable of providing detailed health insights. For example, the latest innovations in blood pressure monitoring emphasize the importance of staying within therapeutic targets of <130/80 mmHg, as suggested by updated international hypertension guidelines. This capability, combined with the push for widespread use of wearables by health authorities, underscores the significant benefits of pressure sensors. They facilitate a proactive approach to health management, ensuring patients and providers can effectively collaborate on treatment plans that account for real-time physiological data.
When selecting a pressure sensor, several critical factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance for specific applications. One of the primary considerations is the measurement range. Pressure sensors come in various ranges, and choosing one that accurately encompasses the expected operational pressures is essential. According to a recent market analysis, more than 60% of industrial applications require sensors that can handle pressures up to 100 bar, highlighting the necessity for careful range selection.
Another vital factor is the sensor's accuracy and precision. Pressure sensors are typically designed with varying degrees of accuracy, often expressed as a percentage of full scale. Industry reports indicate that high-performance sensors can achieve accuracy levels of up to ±0.1% FS, making them suitable for critical applications in pharmaceuticals and aerospace, where even slight variations could lead to significant issues. Additionally, temperature compensation and long-term stability are crucial, especially in environments subject to drastic temperature fluctuations, as they directly affect sensor reliability and performance over time.
| Sensor Type | Operating Principle | Typical Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piezoresistive | Changes in electrical resistance under mechanical stress. | Automotive, HVAC systems, medical devices. | High accuracy, wide pressure range. |
| Capacitive | Change in capacitance relative to pressure changes. | Consumer electronics, industrial automation. | Compact size, good sensitivity. |
| Strain Gauge | Measures strain on a material that changes resistance. | Structural monitoring, aerospace applications. | Robust, reliable under extreme conditions. |
| Optical | Uses light intensity changes to measure pressure. | Oil and gas, chemical processing. | Immune to electromagnetic interference. |
| Differential | Measures pressure differences between two points. | Medical applications, environmental monitoring. | Precise differential measurements. |
As a specialist in environmental and flow sensor technology, ScioSense enables companies to use the planet’s resources more sustainably, helping to create a healthier future for all.