Choosing the right digital pressure sensors is crucial for many applications. These sensors measure pressure accurately and provide valuable data. With so many options available, it can feel overwhelming.
Consider your specific needs when selecting a digital pressure sensor. Factors such as pressure range, accuracy, and application type play key roles. Some sensors excel in extreme environments but may lack in others. This can lead to performance issues.
Reflect on your long-term goals as well. Are you looking for durability or precision? Understanding your requirements will help narrow your choices. Making an informed decision can save time and resources in the long run. Choosing wisely today can prevent frustrations tomorrow.

Digital pressure sensors play a crucial role in numerous applications. These sensors measure pressure with high accuracy. They convert pressure into digital signals. This allows for easy integration into various systems. Understanding how these sensors work is essential.
Digital pressure sensors can vary in types and specifications. Some offer absolute pressure measurement, while others measure gauge pressure. It’s important to recognize your needs before selecting one. Factors such as range, accuracy, and response time matter greatly. Inappropriate choices can lead to inaccurate data. Testing the sensors under real conditions can reveal surprising limitations.
Besides technical specifications, consider installation and compatibility issues too. The environment also impacts performance. Humidity, temperature, and potential exposure to corrosive elements can affect readings. Evaluate these conditions comprehensively. Choosing the right digital pressure sensor requires thoughtfulness and a bit of trial and error to find the best match.
When choosing digital pressure sensors, key specifications are crucial. One important factor is accuracy. According to industry data, a sensor's accuracy can significantly impact performance, with some sensors offering 0.01% FS. This level of precision is ideal for critical applications like industrial processes and aerospace.
Another important specification is the range. Sensors come in various pressure ranges, from vacuum up to thousands of psi. Knowing your application's requirements is essential. For example, if a sensor operates within a 0-100 psi range, select one that covers this without excessive overhead.
Response time is another critical aspect. Many sensors have response times between 1 to 1000 milliseconds. In dynamic environments, a fast response is often necessary to make real-time adjustments. Be cautious, however, as faster speeds can sometimes lead to trade-offs in durability or robustness.
Lastly, consider the operating temperature range. Some sensors can operate in extreme conditions, while others may fail at high temperatures. It's essential to match the sensor’s capabilities with your environmental conditions. Choosing the right sensor involves careful consideration of these specifications to avoid potential future complications.
| Specification | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Range | The minimum and maximum pressure levels the sensor can measure. | Critical for ensuring the sensor is suitable for your application. |
| Accuracy | The degree to which the sensor's measurements reflect the true pressure. | Essential for applications requiring precise pressure measurements. |
| Output Type | The type of signal output (e.g., analog, digital, or wireless). | Determines compatibility with your existing systems. |
| Temperature Range | The range of temperatures in which the sensor can operate effectively. | Important for applications in varying environmental conditions. |
| Mounting Style | The method by which the sensor is installed (e.g., threaded or flush). | Affects installation convenience and space requirements. |
| Wetted Materials | Materials that come in contact with the measured pressure media. | Ensures compatibility with the fluid to prevent corrosion or contamination. |
| Power Supply | The voltage and type of power source required for the sensor. | Important for ensuring the sensor can be powered in your setup. |
Digital pressure sensors come in various types, each tailored for specific applications. One common type is the piezoresistive sensor. It works on the principle of resistance change with pressure. Often used in automotive and industrial applications, these sensors provide reliable measurements. According to a recent industry report, the demand for piezoresistive sensors is expected to grow by 5% annually.
Another prevalent type is capacitive pressure sensors. These sensors utilize a capacitor to measure pressure changes. They are known for high accuracy and stability. Many industries, such as aerospace and medical, depend on their precise readings. Yet, their sensitivity can lead to challenges in highly fluctuating environments.
Membrane pressure sensors are also noteworthy. They are often used in harsh conditions. Their robust design provides significant advantages in outdoor applications. However, users should consider how environmental factors may affect their performance. An interesting statistic from a market research study shows that membrane sensors hold about 20% of the overall market share. Each type serves diverse purposes, but factors like accuracy, environment, and application must be carefully evaluated.
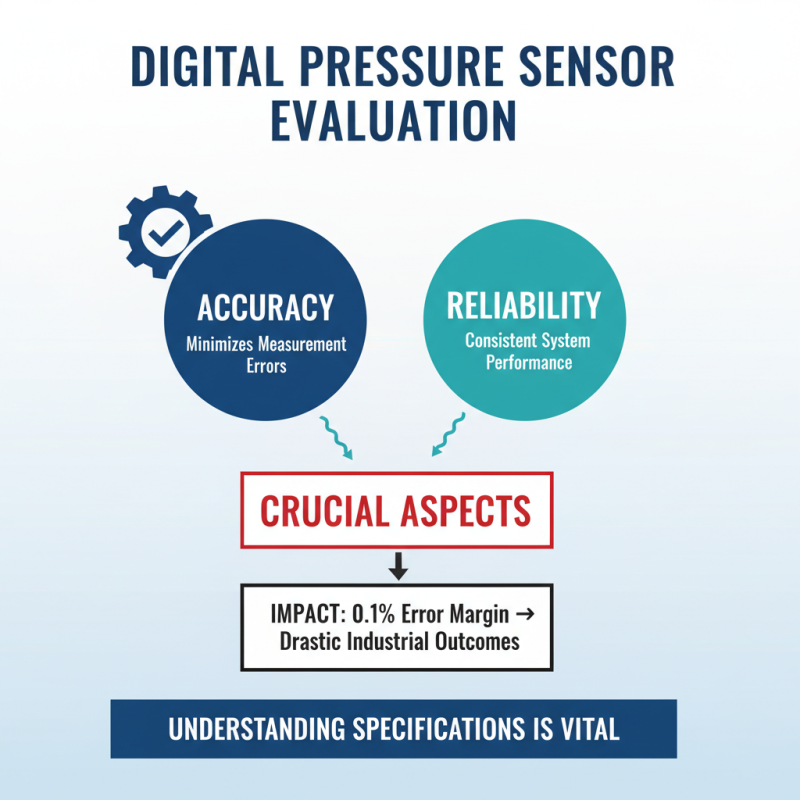
When evaluating digital pressure sensors, accuracy and reliability are crucial aspects. A report indicates that inaccuracies can lead to significant measurement errors, affecting system performance. For example, an error margin as low as 0.1% can drastically alter industrial outcomes. Therefore, understanding the specifications is vital.
Consider the sensor's calibration range. Some sensors may provide reliable measurements only within a narrow range. Using sensors outside this range can compromise accuracy. Regular calibration is essential to maintain sensor performance. Research shows that frequent re-calibration helps sustain accuracy over time.
Furthermore, sensor reliability is not merely about accuracy. Environmental factors play a role too. Exposure to extreme temperatures or humidity can affect sensor readings. Over 30% of sensor failures stem from environmental stresses. Proper shielding and housing can mitigate these risks. Yet, not all sensors can withstand harsh conditions. Users need to reflect on their specific application environments when selecting a digital pressure sensor.
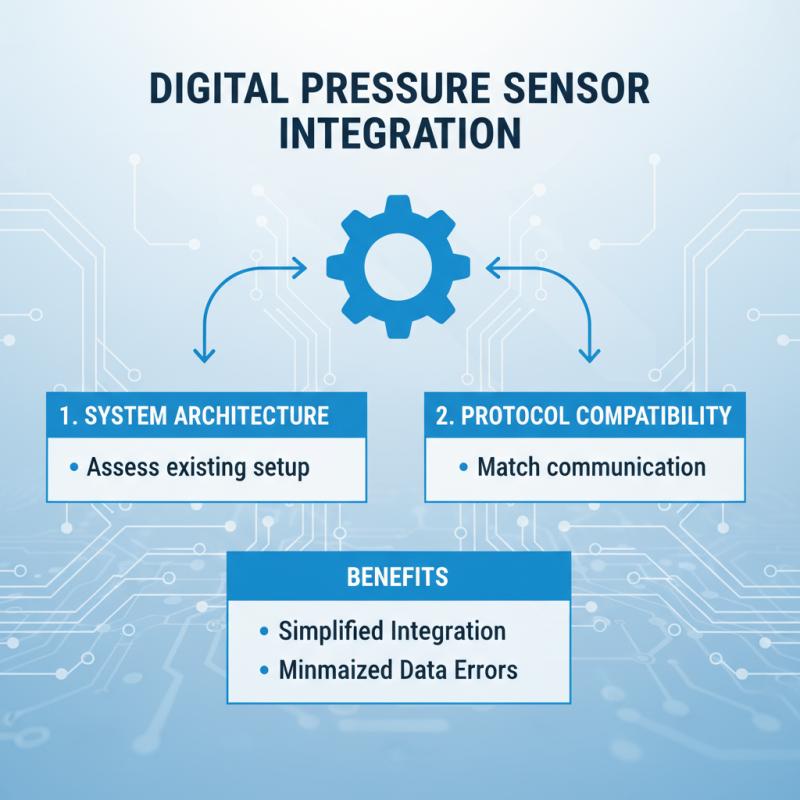
When integrating digital pressure sensors into your systems, it’s crucial to consider compatibility. Assess your system's existing architecture. Ensure the digital pressure sensor matches the communication protocols in use. This simplifies integration and minimizes data transmission errors.
When choosing sensors, focus on their specific range and resolution. Think about your application's pressure variability. Some sensors handle high pressure better than others. This may lead to performance issues or inaccurate measurements if mismatched.
Tips for integration include testing sensors in real conditions before full deployment. This approach allows minor adjustments to be made ahead of time. Ensure that you have appropriate software tools to process the data. Sometimes, even small coding errors can lead to significant issues. Regularly review your setup to capture any unexpected behaviors.





As a specialist in environmental and flow sensor technology, ScioSense enables companies to use the planet’s resources more sustainably, helping to create a healthier future for all.