In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation and process control, the importance of accurate temperature measurement cannot be overstated. Temperature measurement sensors are pivotal in ensuring operational efficiency, safety, and product quality across various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and manufacturing. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global temperature sensor market is projected to grow from $5.6 billion in 2020 to $9.1 billion by 2026, reflecting an increasing reliance on precision measurement technologies.
When selecting the right temperature measurement sensors for your specific applications, it is crucial to consider several factors that can impact performance and reliability. These may include the sensor type, measurement range, response time, and environmental conditions. With advancements in technology, such as the development of smart sensors and wireless monitoring solutions, businesses are now better equipped to manage temperature measurements more effectively. Understanding these elements is essential for making informed decisions that align with your operational needs and objectives, ultimately leading to improved productivity and compliance with industry standards.

When selecting temperature measurement sensors, it is crucial to understand the various types available in the market. The three primary categories of temperature sensors are contact, non-contact, and smart sensors. Contact sensors, such as thermocouples and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), provide direct measurement by making physical contact with the measured object. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the thermocouple market is expected to reach USD 1.57 billion by 2025, highlighting its widespread application in industrial settings due to its robustness and fast response times.
On the other hand, non-contact sensors, including infrared sensors, measure temperature from a distance without direct contact. These sensors are increasingly favored in dynamic environments where contact measurements may not be practical or safe. The global non-contact temperature sensor market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2020 to 2025, driven by their adoption in industries such as food processing and HVAC systems. Lastly, smart sensors, equipped with advanced technologies like IoT connectivity, are transforming temperature measurement by enabling remote monitoring and data analytics, thereby enhancing process efficiency. The integration of these smart solutions is forecasted to revolutionize the temperature sensor market, promoting safer and more efficient industrial operations.
| Sensor Type | Temperature Range | Accuracy | Response Time | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermocouple | -200 to 1750 °C | ±1.5 °C | Fast | Industrial, HVAC |
| RTD | -200 to 850 °C | ±0.1 °C | Medium | Laboratories, Food Safety |
| Thermistor | -55 to 125 °C | ±0.5 °C | Very Fast | Consumer Electronics, Medical |
| Infrared Sensors | -40 to 1000 °C | ±2 °C | Instant | Non-Contact Measurements |
| Bimetallic Sensors | -50 to 600 °C | ±3 °C | Medium | HVAC, Industrial |
| Silicon Sensors | -55 to 150 °C | ±0.5 °C | Fast | Consumer Electronics |
| Embedded Sensors | -40 to 125 °C | ±2 °C | Varies | Automotive, Aerospace |
| Wireless Sensors | -40 to 125 °C | ±1 °C | Real-time | Smart Homes, IoT |
| Contact Sensors | -200 to 600 °C | ±1 °C | Medium | Manufacturing, Food Processing |
When selecting temperature measurement sensors, evaluating the accuracy and precision requirements for your application is crucial. Accuracy refers to how close a sensor's readings are to the true temperature, while precision indicates how consistently a sensor can reproduce measurements. According to a 2022 report by the International Society of Automation (ISA), industrial applications require sensors to achieve a minimum accuracy of ±0.5°C to ensure operational efficiency and safety. In laboratory settings, where even slight variances can lead to significant results, a ±0.1°C accuracy is often deemed necessary.
Moreover, understanding the environment where the sensors will be employed is vital. For instance, sensors placed in extreme temperatures or varying atmospheric conditions may require enhanced specifications to maintain their accuracy. The same ISA report highlights that non-contact infrared thermometers can lose accuracy in highly reflective environments, thereby necessitating an evaluation of materials and surfaces when selecting a sensor type. By taking these factors into account, organizations can better align their sensor choice with their accuracy and precision needs, ensuring reliable data collection and enhancing operational performance across various applications.
When choosing temperature measurement sensors, it's crucial to assess the environmental conditions where the sensors will be deployed. Factors such as humidity, pressure, and potential exposure to chemicals or extreme temperatures can significantly impact the sensor's performance and longevity. For instance, sensors placed in high-humidity environments may require additional protection to prevent condensation, which could affect accuracy. Understanding these environmental conditions helps in selecting sensors that can withstand specific challenges, ensuring reliable readings over time.
Another important consideration is the physical location of the sensors. If sensors are installed outdoors, they need to be robust enough to handle UV exposure, precipitation, and varying temperatures. Conversely, sensors used in controlled indoor environments may not need the same level of protection. Furthermore, proximity to heat sources or airflow can influence temperature readings, so careful planning of sensor placement is imperative. Assessing these environmental factors not only aids in selecting the right sensor type but also ensures optimal performance and data integrity throughout its operational life.
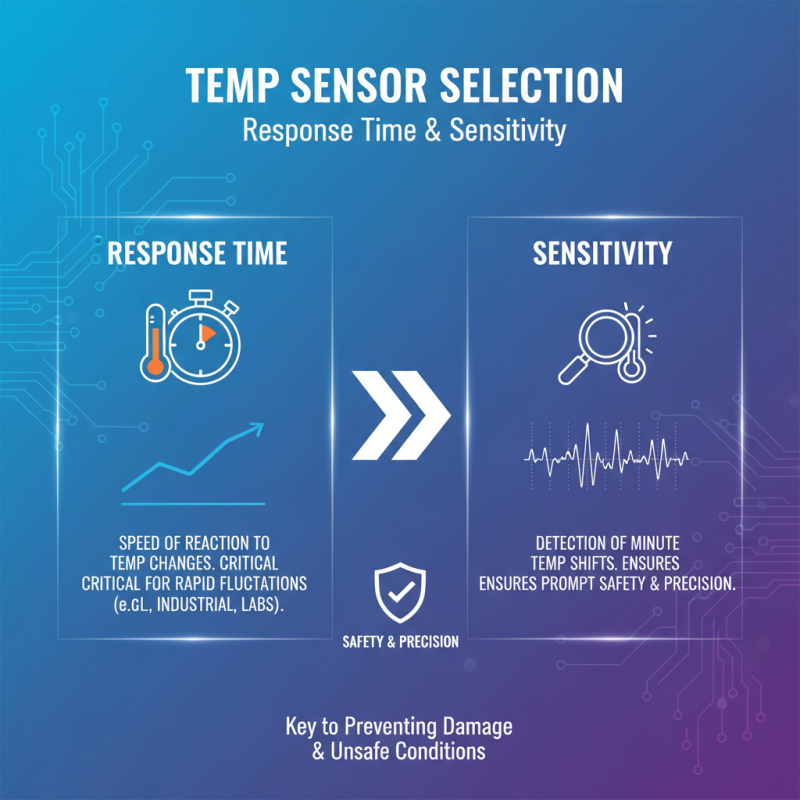
When selecting temperature measurement sensors, understanding the importance of response time and sensitivity is crucial. Response time refers to how quickly a sensor can react to temperature changes, which is vital in applications where temperature fluctuations occur rapidly. For instance, in industrial processes or critical laboratory environments, a sensor with a faster response time can help ensure that safety measures are promptly implemented, reducing the risk of damage or unsafe conditions.
When evaluating sensors, consider the following tips: first, assess the environment where the sensor will be used. If temp changes are quick, opt for sensors known for their swift response capabilities, like thermocouples or infrared sensors. Second, think about the sensitivity level required for your application. If you're monitoring subtle temperature variations, choose sensors with high sensitivity to guarantee accurate readings. Lastly, don't forget about the calibration and maintenance of the sensors, as this can affect their response time and sensitivity over time.
Selecting the right temperature measurement sensors hinges on carefully balancing response time and sensitivity according to your specific requirements. By focusing on these aspects, you can ensure accurate and timely temperature monitoring, tailored to your operational needs.
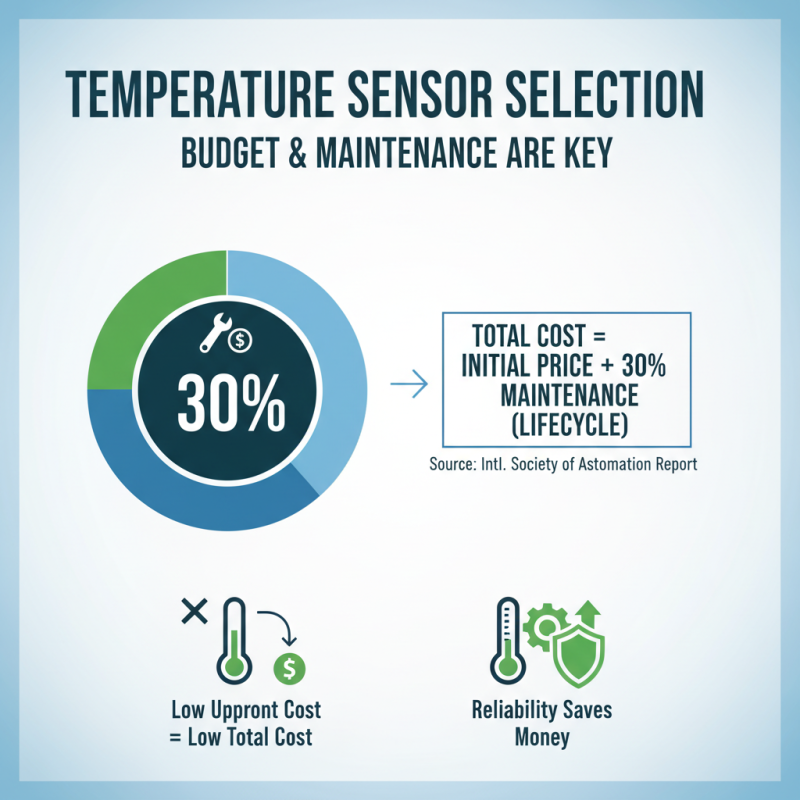
When selecting temperature measurement sensors, considering budget and maintenance factors is paramount. According to a report by the International Society of Automation, approximately 30% of the total cost of temperature sensing solutions is attributed to long-term maintenance and operational expenses. This statistic underscores the importance of not only the initial purchase price but also the total cost of ownership over the sensor’s lifecycle. For example, sensors that require frequent calibration or replacement can quickly diminish savings from lower upfront costs, thereby affecting your overall budget.
Moreover, sensor reliability directly correlates with maintenance frequency and associated costs. A study by the American Society for Quality found that operational disruptions attributed to sensor failures can lead to losses of up to 20% in productivity. Therefore, investing in higher-quality sensors may yield lower maintenance needs, ensuring consistent temperature accuracy and extending the sensor's service life. Evaluating the reliability and maintenance requirements when choosing temperature sensors can ultimately lead to more informed decisions that balance performance with cost-effectiveness, ensuring a sustainable investment for your specific applications.






As a specialist in environmental and flow sensor technology, ScioSense enables companies to use the planet’s resources more sustainably, helping to create a healthier future for all.