Capacitance sensors have become an integral part of various modern applications, serving as reliable solutions for measuring and detecting various physical parameters. These sensors operate based on the principle of capacitance, which involves the storage of electrical charge and the variation of electric fields. By understanding how capacitance sensors function, users can harness their unique capabilities to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of numerous systems ranging from industrial automation to consumer electronics.
The versatility of capacitance sensors allows them to be utilized in diverse fields, including proximity sensing, level detection, and touch interfaces. Their ability to detect changes in capacitance enables precise measurements of distance and presence, making them invaluable in applications such as liquid level monitoring and user interface design. As technology continues to evolve, the potential applications for capacitance sensors expand, further enhancing their importance in contemporary engineering and design solutions.
In this article, we will delve into the key operating principles of capacitance sensors, explore their various applications, and discuss how they contribute to advancements in technology. By gaining a deeper understanding of these sensors, professionals across multiple industries can better implement and benefit from these sophisticated tools in their practices.

Capacitance sensors are versatile devices that detect changes in capacitance, which is the ability of a system to store an electrical charge. These sensors work on the principle that the capacitance between two conductive plates changes when a dielectric material, such as a human body or an object, approaches or touches the sensor. The primary function of capacitance sensors is to convert this change in capacitance into an electrical signal that can be processed and interpreted. This makes them incredibly useful in a wide array of applications, from touch-sensitive switches in consumer electronics to level measurement in industrial processes.
When working with capacitance sensors, it's essential to consider environmental factors that could affect their performance. For example, moisture in the air can lead to false readings, so ensuring a clean and dry environment may enhance their reliability. Additionally, the materials surrounding the sensor can impact its sensitivity. A more conductive material nearby may cause interference, while non-conductive materials can enhance performance.
Tips: To optimize the functionality of capacitance sensors, experiment with different mounting positions and spacing from surrounding objects. Calibration is key—periodically check and adjust your sensor settings to account for changes in the environment or application over time. Establishing baseline readings can also help identify and mitigate any anomalies in sensor performance.
Capacitance sensors are widely used in various applications due to their unique operating principles. At the core of these sensors is the capacitor, which consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulator. When a dielectric material, such as air or another medium, is introduced between the plates, it alters the capacitance value. This change is proportional to the amount of dielectric present, making capacitance sensors effective for measuring proximity, displacement, and level.
The key components of capacitance sensors include the sensing electrodes, the dielectric material, and the electronic circuitry that processes the changes in capacitance. When an object approaches the sensor, the dielectric constant changes, leading to a shift in the capacitance reading. The electronic components translate this variation into a measurable output signal, which can be calibrated for specific applications like touch screens, liquid detection, or proximity sensing.
Tips: When implementing capacitance sensors, consider the environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, which can affect performance. Proper calibration and shielding can help minimize the influence of external conditions, ensuring accurate measurements. Always test the sensor in the intended environment to achieve reliable results.
| Key Component | Description | Operating Principle | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacitance Plate | Two conductive plates that store electrical charge. | Capacitance changes with the distance between plates or dielectric medium. | Proximity sensing, level measurement. |
| Dielectric Material | Insulating material that separates the plates and affects capacitance. | Changes in dielectric constant alter capacitance readings. | Touch sensing, fluid level detection. |
| Sensor Circuit | Electronic circuitry that processes capacitance signals. | Converts changes in capacitance to a measurable output. | Industrial automation, consumer electronics. |
| Output Signal | Signal indicating the capacitance level, often in voltage or frequency. | Reflects the changes in sensor input, indicating proximity or level. | Automated systems, smart appliances. |
Capacitance sensors are renowned for their versatility and precision, finding applications across various industries. In the food and beverage sector, for instance, these sensors are utilized to detect the level of liquid in tanks and ensure that the filling process is both accurate and efficient. Their non-contact nature allows them to measure the presence or absence of liquids without risking contamination, making them ideal for environments where hygiene is paramount.
In the automotive industry, capacitance sensors play a critical role in enhancing safety and convenience. They are often employed in proximity sensing applications, such as automatic parking systems and collision detection features, where accurate detection of objects around a vehicle is essential. Additionally, they can be used in touch-sensitive controls within vehicles, providing a seamless user experience that minimizes the need for physical buttons and switches.
Moreover, capacitance sensors are increasingly being integrated into smart home technology. These sensors facilitate the automation of lighting and HVAC systems by detecting human presence or motion, allowing for energy-efficient management of home environments. Their ability to operate behind surfaces or within materials further expands their applicability, enabling innovative designs that enhance both functionality and aesthetic appeal in smart homes.
Capacitance sensors have emerged as vital tools across various industries, primarily due to their precision and reliability in measuring changes in capacitance. Various industry standards and specifications govern their use, ensuring safety and performance compliance. For instance, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) outlines specific standards, such as IEC 61000, which address electromagnetic compatibility—critical for sensors used in environments with high levels of electronic interference. Additionally, the IEEE 1720 standard provides guidance on the design and testing of capacitive sensors, helping manufacturers create devices that meet safety and performance expectations.
The growing adoption of capacitance sensors in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics underscores the importance of adhering to these standards. According to a recent market report, the global capacitance sensor market is projected to reach USD 2 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4% from 2020 to 2025. This growth aligns with the increased demand for accurate sensing solutions, highlighting the need for strict compliance with established guidelines. Ensuring sensors meet these specifications not only enhances their reliability but also augments user confidence in their applications across various high-tech fields.
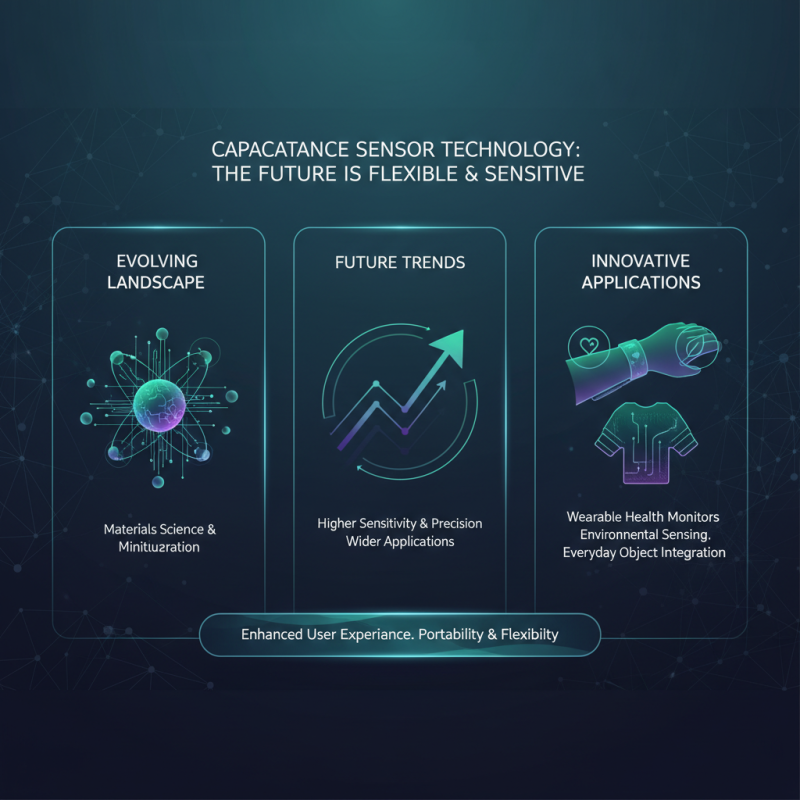
The landscape of capacitance sensor technology is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in materials science and miniaturization techniques. Future trends indicate a shift towards higher sensitivity and more precise detection capabilities, allowing these sensors to be integrated into a wider array of applications. Innovations in flexible electronics will enable capacitance sensors to be incorporated into wearable devices, providing real-time health monitoring and environmental sensing. This shift towards flexibility and portability is expected to enhance user experience and broadens the potential for integration into everyday objects.
Furthermore, the development of smart capacitance sensors is set to revolutionize industrial applications. With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT), these sensors can be networked with other systems, facilitating remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. Advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques are being implemented alongside capacitance technology to improve data interpretation, leading to more informed decision-making in various sectors, from automation to agriculture. As the demand for smart and efficient solutions grows, capacitance sensor technology will play a crucial role in shaping the future of smart environments and sustainable practices.





As a specialist in environmental and flow sensor technology, ScioSense enables companies to use the planet’s resources more sustainably, helping to create a healthier future for all.