As we look towards 2026, the landscape of smart technology applications is evolving rapidly. Commonly used sensors are at the heart of this transformation. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global sensor market is projected to reach $388.9 billion by 2025, driven by innovations and demand for efficiency. These sensors enable devices to collect data, interact with users, and respond to environments intelligently.
Among commonly used sensors, temperature, pressure, and motion sensors stand out. They are crucial for industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and home automation. For example, in smart homes, motion sensors can enhance security while optimizing energy use. However, the selection of sensors is not without challenges. Factors such as accuracy, cost, and integration complexities often require careful consideration.
The increasing prevalence of the Internet of Things (IoT) also necessitates a reevaluation of sensor technologies. While the opportunities are vast, organizations must remain vigilant about compatibility and data privacy issues. As we advance, openly addressing these concerns will be essential for harnessing the full potential of commonly used sensors in smart technology applications.

Smart technology is transforming industries globally. Sensors play a crucial role in this evolution. According to a report from MarketsandMarkets, the smart sensor market is projected to reach $53.5 billion by 2026. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on sensors in various applications.
These sensors collect real-time data. They make systems smarter and more efficient. For instance, temperature sensors help in managing energy consumption. They ensure optimal heating and cooling in smart buildings. A study from IDTechEx suggests that smart cities will rely heavily on sensors for resource management. This reliance raises questions about data privacy and security.
The integration of sensors in wearables is another notable trend. These devices monitor health metrics and track fitness levels. However, many users are unaware of data collection practices. Transparency is essential for user trust. The misuse of data can undermine the benefits of sensor technology. Developers must address these concerns for wider adoption.
Sensors play a crucial role in smart technology applications. These devices gather data and enhance system functionality. Commonly used sensors include temperature, proximity, and humidity sensors. According to industry reports, the global sensor market is projected to reach $400 billion by 2026.
Temperature sensors are vital for climate control in smart homes. They help maintain comfortable living conditions. Proximity sensors, meanwhile, enable devices to detect physical presence. This technology is useful in security systems and automated lighting. Humidity sensors monitor air moisture levels. High humidity can lead to mold growth, a common problem in many homes.
However, not all sensors perform perfectly. Calibration issues can lead to inaccuracies. Sensor placement is another critical factor. Poor placement can result in unreliable data. As sensor technology evolves, addressing these imperfections will be essential. The integration of advanced algorithms may help improve performance.
In smart technology applications, sensors play a crucial role in gathering data. The effectiveness of sensors depends on key features and specifications. For instance, accuracy and sensitivity are paramount. According to recent industry reports, sensors with high accuracy can reduce error rates by up to 30%. This directly impacts the performance of smart devices.
Another vital specification is the response time. The quicker the sensor, the more responsive the device. For smart-home systems, a response time of less than 50 milliseconds is ideal. Such speed can enhance user experiences dramatically. It’s worth noting that not all sensors can meet these criteria. Some may struggle in challenging environments.
**Tip:** Always assess the environmental conditions where the sensor will be deployed. Compatibility with temperature and humidity levels can make a big difference.
Power consumption is also a key consideration. Many effective sensors are designed to be energy-efficient. Reports indicate that low-power sensors can extend battery life by up to 40%. Yet, this comes with a trade-off in some cases, such as processing speed. Striking a balance here is essential.
**Tip:** Look for sensors that offer adjustable settings. This helps you optimize performance based on your specific application needs.
| Sensor Type | Key Features | Specifications | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Sensor | High accuracy, wide temperature range, quick response time | -40°C to 125°C, ±0.5°C accuracy | HVAC systems, wearable devices, smart thermostats |
| Motion Sensor | Passive infrared, wide detection angle, low power consumption | Detection range: up to 12m, angle: 120° | Security systems, automatic lighting, smart homes |
| Humidity Sensor | High stability, fast response, integrated temperature compensation | 0% to 100% RH, ±3% RH accuracy | Weather stations, air conditioning, greenhouses |
| Light Sensor | Wide dynamic range, low light sensitivity, analog output | 1 to 100,000 lux, response time: < 10 ms | Smart lighting, display brightness adjustment, agricultural monitoring |
| Gas Sensor | Selectivity for specific gases, low power dissipation, fast response | Detection range: 0-1000 ppm, response time: < 10s | Air quality monitoring, industrial safety, smart homes |
In 2026, sensor technology is set to transform various smart applications. Compact and efficient sensors will enhance connectivity in smart homes and cities. Wireless sensors, capable of real-time data collection, will become commonplace. They can streamline operations, but challenges remain. Data privacy and security concerns are more prominent than ever. As sensors gather more personal data, user trust may waver.
The integration of AI in sensors is a key trend. These intelligent devices will analyze data instantly, leading to faster decision-making. Smart health monitoring systems will use sensors to track vital signs continuously. While this sounds promising, accuracy issues can arise. Misinterpretation of sensor data could lead to incorrect health assessments. Users may need to double-check readings from time to time.
Energy-efficient sensors will rise in popularity as sustainability becomes crucial. Long-lasting, low-power sensors are essential for remote applications. However, ensuring reliable performance under varied conditions can be tricky. Developers may face hurdles in balancing efficiency with functionality. Smart technology will continue to evolve, yet challenges in sensor accuracy and reliability will require ongoing attention.
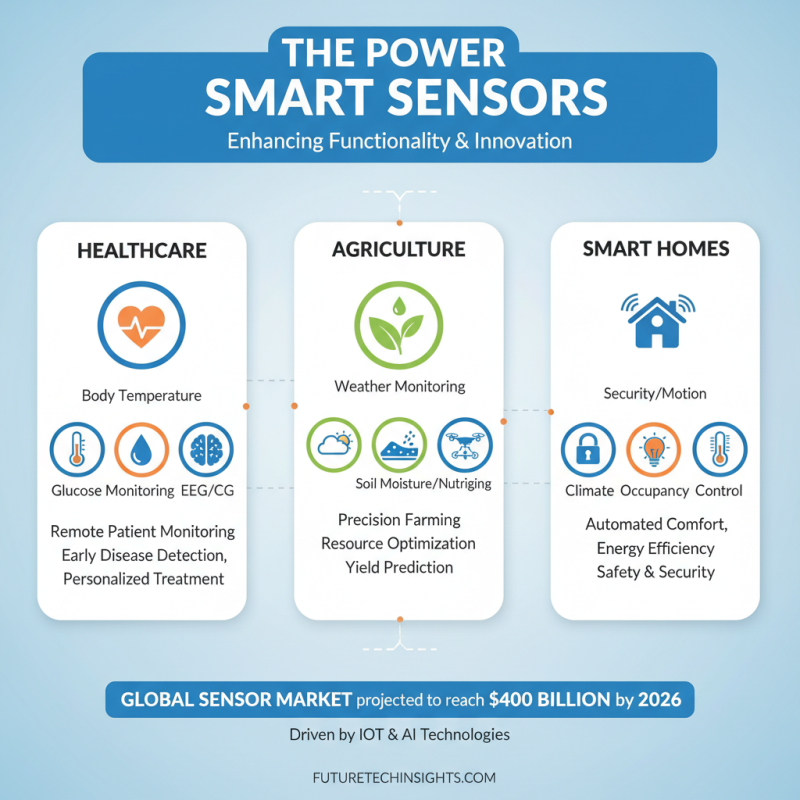
Smart technology integrates various sensors to enhance functionality across multiple applications. These sensors play a crucial role in fields like healthcare, agriculture, and smart homes. According to a recent report, the global sensor market is expected to reach $400 billion by 2026, driven by increases in IoT and AI technologies.
In healthcare, sensors monitor patient vitals remotely. Wearables track heart rate and other critical data. Farmers use soil moisture sensors to optimize irrigation. This tech can save up to 30% on water usage. Smart homes leverage temperature and motion sensors for energy efficiency and security. Data reveals that homes equipped with smart sensors can reduce energy consumption by 15% yearly.
Tips: Always consider sensor accuracy. Calibration can greatly impact performance. Additionally, ensure compatibility with existing systems when integrating new sensors. Balancing cost and quality is essential. Sometimes, cheaper options may not meet the required standards, leading to failures. Regularly assess the sensor's effectiveness to avoid reliance on faulty data.





As a specialist in environmental and flow sensor technology, ScioSense enables companies to use the planet’s resources more sustainably, helping to create a healthier future for all.